Acceleration - practice problems
Acceleration is the rate at which an object's velocity changes over time, measured in meters per second squared (m/s²). It occurs when an object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction. Positive acceleration increases velocity, while negative acceleration (deceleration) reduces it. Force causes acceleration, as described by Newton's second law: F = ma (force equals mass times acceleration). Examples include a car speeding up, a ball falling under gravity, or a planet orbiting the sun.Number of problems found: 254
- 4100 USD
 4100 USD was distributed in 50 boys and girls. Each boy got $ 90 and each girl $ 65. Then, find the number of boys.
4100 USD was distributed in 50 boys and girls. Each boy got $ 90 and each girl $ 65. Then, find the number of boys. - Five men
 5 men or 9 women can do a piece of work in 19 days, in how many days will 3 men and 6 women do it?
5 men or 9 women can do a piece of work in 19 days, in how many days will 3 men and 6 women do it? - Cement, sand, and gravel
 Concrete tiles are made using buckets of cement, sand, and gravel mixed in a ratio of 1:4:6. How many buckets of gravel are needed for 4 buckets of cement?
Concrete tiles are made using buckets of cement, sand, and gravel mixed in a ratio of 1:4:6. How many buckets of gravel are needed for 4 buckets of cement? - The ratio 20
 The ratio of the boys to the girls is 1:3. There are 20 pupils. How many boys and how many girls are there?
The ratio of the boys to the girls is 1:3. There are 20 pupils. How many boys and how many girls are there? - One half of students
 There are 1200 students in the school. Of which 600 are girls. Find the percentage of boys.
There are 1200 students in the school. Of which 600 are girls. Find the percentage of boys. - Known hcf and find lcm
 Given that HCF (306, 657) = 9, find LCM (306, 657).
Given that HCF (306, 657) = 9, find LCM (306, 657). - Students 48
 If 80% of the students of a school are boys and 225 are girls, find the number of all students.
If 80% of the students of a school are boys and 225 are girls, find the number of all students. - A baby
 A baby weighs 8 and 1/4 pounds at birth. Two weeks later, she weighs 8 and 7/8 pounds. How much did the baby gain?
A baby weighs 8 and 1/4 pounds at birth. Two weeks later, she weighs 8 and 7/8 pounds. How much did the baby gain? - A bag 6
 A bag contains 3 red marbles, 8 blue marbles, and 5 green marbles. If two marbles are drawn out of the bag, what is the probability, to the nearest 1000th, that both marbles drawn will be blue?
A bag contains 3 red marbles, 8 blue marbles, and 5 green marbles. If two marbles are drawn out of the bag, what is the probability, to the nearest 1000th, that both marbles drawn will be blue? - Geometric 20
 Find the geometric mean of 15 15 20 25 30.
Find the geometric mean of 15 15 20 25 30. - Daniw
 Daniw Elementary School has a total of 98 pupils. If 3/7 of them are boys, how many of the pupils are girls?
Daniw Elementary School has a total of 98 pupils. If 3/7 of them are boys, how many of the pupils are girls? - FGH right triangle
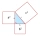 Given a right triangle with leg lengths f and g, and hypotenuse h, if f = 7 cm and h = 11.2 cm, what is g?
Given a right triangle with leg lengths f and g, and hypotenuse h, if f = 7 cm and h = 11.2 cm, what is g? - There 34
 There were 90 children at the birthday party. If 3/5 of them were boys, how many were girls?
There were 90 children at the birthday party. If 3/5 of them were boys, how many were girls? - The number 8
 The number of sheep is x. The number of goats is thrice the number of sheep. Write an expression for the number of goats.
The number of sheep is x. The number of goats is thrice the number of sheep. Write an expression for the number of goats. - Pupils
 There are 40 pupils in a class. 30% of them are boys. How many pupils in the class are girls?
There are 40 pupils in a class. 30% of them are boys. How many pupils in the class are girls? - Z-score calc
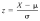 What is the Z Score for the following numbers: X is 16, and data for the population mean, and the standard deviation is 196, 193, 79, 30, 29, 81, 25, 21, 164 Level of difficulty = 2 of 2 Please format it to 2 decimal places.
What is the Z Score for the following numbers: X is 16, and data for the population mean, and the standard deviation is 196, 193, 79, 30, 29, 81, 25, 21, 164 Level of difficulty = 2 of 2 Please format it to 2 decimal places. - Carol 2
 Carol bought 5 snow hats and 2 pairs of gloves. The hats were priced at $12, and each pair of gloves cost the same amount. If the total amount of Carol's purchase is $135, what was the cost of 1 pair of gloves?
Carol bought 5 snow hats and 2 pairs of gloves. The hats were priced at $12, and each pair of gloves cost the same amount. If the total amount of Carol's purchase is $135, what was the cost of 1 pair of gloves? - The ratio 14
 The ratio of boys to girls is 8:7. If there are 40 boys, how many girls are there in the class?
The ratio of boys to girls is 8:7. If there are 40 boys, how many girls are there in the class? - The ratio 13
 The ratio of boys to girls in Mr. Hakeem's class is 6:4. If there are 18 boys, how many girls are there?
The ratio of boys to girls in Mr. Hakeem's class is 6:4. If there are 18 boys, how many girls are there? - Native plants
 In a garden, 5/6 of the area is filled with native plants. The native plants take up 107/4 m². Let g represent the total area of the garden. Find g = total area of the garden.
In a garden, 5/6 of the area is filled with native plants. The native plants take up 107/4 m². Let g represent the total area of the garden. Find g = total area of the garden.
Do you have unsolved math question and you need help? Ask a question, and we will try to solve it. We solve math question.
