Quadratic equation calculator
Quadratic equation has the basic form: ax2+bx+c=0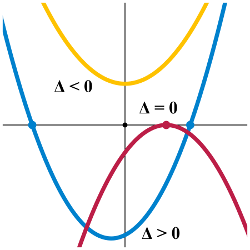
Calculation:
Solution in text:
x2-x-30=0 ... quadratic equationDiscriminant:
D = b2 - 4ac = 121
D > 0 ... The equation has two distinct real roots
x1 = 6
x2 = -5
P = {6; -5}
