Quadratic equation calculator
Quadratic equation has the basic form: ax2+bx+c=0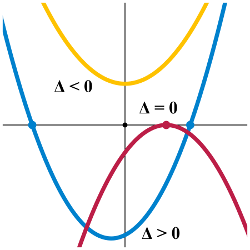
Calculation:
140=3∗sqrt(3)∗a2+30a −5.1961524227066a2−30a+140=0 5.1961524227066a2+30a−140=0 p=5.196152;q=30;r=−140 D=q2−4pr=302−4⋅5.196152⋅(−140)=3809.8453567157 D>0 a1,2=2p−q±D=10.392305−30±3809.85 a1,2=−2.886751±5.939389 a1=3.052638008 a2=−8.8261407 Factored form of the equation: 5.1961524227066(a−3.052638008)(a+8.8261407)=0
Solution in text:
-5.1961524227066a2-30a+140=0 ... quadratic equationDiscriminant:
D = b2 - 4ac = 3809.8453567157
D > 0 ... The equation has two distinct real roots
a1 = 3.052638
a2 = -8.8261407
P = {3.052638; -8.8261407}
