Vector - practice problems
A vector is a mathematical object with both magnitude (length) and direction, often represented as an arrow in space or by coordinates. Vectors are denoted in various ways including bold letters (v), arrows (→v), or component form ⟨x, y⟩ or ⟨x, y, z⟩. Vector operations include addition (tip-to-tail or component-wise), scalar multiplication, dot product (yielding a scalar), and cross product (yielding a vector, in 3D). Vectors are fundamental to physics for representing quantities like velocity, force, and acceleration. Applications span engineering, computer graphics, navigation, and machine learning. Understanding vectors includes concepts of magnitude, direction, unit vectors, and linear combinations forming vector spaces.Directions: Provide a careful solution to each problem, showing all steps in your work.
Number of problems found: 127
- Vertical components
 Find the horizontal and vertical components of the vector which has magnitude 750 as shown in the following figure.
Find the horizontal and vertical components of the vector which has magnitude 750 as shown in the following figure. - Parallel lines - dist
 Find the distance between the parallel lines 3x – 4y +7 = 0 and 3x – 4y + 5 = 0
Find the distance between the parallel lines 3x – 4y +7 = 0 and 3x – 4y + 5 = 0 - A boat 2
 A boat can travel with a speed of 13 km/h in still water.If the speed speed of stream is 4 km/h, then find the time taken 1) to go 68 km downstream . 2) to go 63 km upstream .
A boat can travel with a speed of 13 km/h in still water.If the speed speed of stream is 4 km/h, then find the time taken 1) to go 68 km downstream . 2) to go 63 km upstream . - The speed 3
 The speed of a boat in still water is 10 km/h. If the boat goes 37.5 km upstream in 5 h, find the speed of the stream.
The speed of a boat in still water is 10 km/h. If the boat goes 37.5 km upstream in 5 h, find the speed of the stream. - EE school boarding
 Three vectors, A, B, and C, are related as follows: A/C = 2 at 120 deg, A + B = -5 + j15, C = conjugate of B. Find C.
Three vectors, A, B, and C, are related as follows: A/C = 2 at 120 deg, A + B = -5 + j15, C = conjugate of B. Find C. - Conjugate coordinates
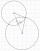 If the rectangular conjugate of the polar vector 12 angle 35 degrees is equal to x+yi, find the sum of x and y.
If the rectangular conjugate of the polar vector 12 angle 35 degrees is equal to x+yi, find the sum of x and y. - Triangle 82
 Triangle PQR has vertices located at (2, 2), (5, -4), and (-4, -1). What type of triangle is triangle PQR?
Triangle PQR has vertices located at (2, 2), (5, -4), and (-4, -1). What type of triangle is triangle PQR? - Matrices 2
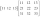 Suppose A=(1 6 3 −2) B=(4 −3 −4 3) find 2A+3B
Suppose A=(1 6 3 −2) B=(4 −3 −4 3) find 2A+3B - Tunnel - quadrilateral
 How long will the tunnel AB be, distances AD=35 m, DC=120 m, CB=85 m, and angles ADC=105 degrees and BCD=71 degrees. ABCD is a quadrilateral.
How long will the tunnel AB be, distances AD=35 m, DC=120 m, CB=85 m, and angles ADC=105 degrees and BCD=71 degrees. ABCD is a quadrilateral. - Calculate 449
 Calculate the size of the angle formed by 2 lines on the dial and formed by connecting the points 7.2 and 1.4.
Calculate the size of the angle formed by 2 lines on the dial and formed by connecting the points 7.2 and 1.4. - Point plane distance
 Calculate the distance of point A[ 4; 2; -3 ] from the plane : 2x - 2y + z + 5 = 0
Calculate the distance of point A[ 4; 2; -3 ] from the plane : 2x - 2y + z + 5 = 0 - Motion on circle
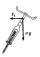 The bend has a radius of r = 100 m and is inclined at an angle of 20° to the horizontal plane (= tilt angle). What is the safe (the "best") speed to go through this curve? Sketch the picture regarding NIVS, mark the forces, and calculate.
The bend has a radius of r = 100 m and is inclined at an angle of 20° to the horizontal plane (= tilt angle). What is the safe (the "best") speed to go through this curve? Sketch the picture regarding NIVS, mark the forces, and calculate. - Calculate cuboid
 Given cuboid ABCDEFGH. We know that |AB| = 1 cm, |BC| = 2 cm, |AE| = 3 cm. Calculate in degrees the angle size formed by the lines BG and FH .
Given cuboid ABCDEFGH. We know that |AB| = 1 cm, |BC| = 2 cm, |AE| = 3 cm. Calculate in degrees the angle size formed by the lines BG and FH . - Ground speed
 The plane flies south at an average speed of 190 km/h, and the wind blows from west to east at a speed of 20 m/s. How fast and in what direction (relative to the meridian) will the plane move relative to the ground?
The plane flies south at an average speed of 190 km/h, and the wind blows from west to east at a speed of 20 m/s. How fast and in what direction (relative to the meridian) will the plane move relative to the ground? - Train speed direction
 Soňa is sitting on the train, looking out the window, and what she doesn't see is that the landscape runs backward at a constant speed of 160 km/h, and on the side track, the train is seemingly backing up at a constant speed of 40 km/h. Sonia stops and wo
Soňa is sitting on the train, looking out the window, and what she doesn't see is that the landscape runs backward at a constant speed of 160 km/h, and on the side track, the train is seemingly backing up at a constant speed of 40 km/h. Sonia stops and wo - Scalar products
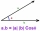 The vectors a = (3, -2), b = (-1, 5) are given. Determine the vector c for which a. c = 17; b . c = 3
The vectors a = (3, -2), b = (-1, 5) are given. Determine the vector c for which a. c = 17; b . c = 3 - Perpendicular forces
 Distribute the force of magnitude F = 100 N into two perpendicular components with magnitudes F1 and F2 so that the angle between forces F1 and F is 43°52'.
Distribute the force of magnitude F = 100 N into two perpendicular components with magnitudes F1 and F2 so that the angle between forces F1 and F is 43°52'. - Triangle height intersection
 Given a triangle ABC: A (-1,3), B(2,-2), C(-4,-3). Determine the coordinates of the intersection of the heights and the coordinates of the intersection of the axes of the sides.
Given a triangle ABC: A (-1,3), B(2,-2), C(-4,-3). Determine the coordinates of the intersection of the heights and the coordinates of the intersection of the axes of the sides. - Operation asterisk pairs
 The * (asterisk) operation assigning one number to two pairs of numbers is introduced as follows: (a, b)*(c, d) = ac+bd We know that: (x,2)*(-1, v) = -1 and (2,-1)*(u, v)=5 and (u, v)*(1,1)=-2 What is (1,2)*(x, y) equal to if y=3?
The * (asterisk) operation assigning one number to two pairs of numbers is introduced as follows: (a, b)*(c, d) = ac+bd We know that: (x,2)*(-1, v) = -1 and (2,-1)*(u, v)=5 and (u, v)*(1,1)=-2 What is (1,2)*(x, y) equal to if y=3? - Crosswind
 A plane is traveling 45 degrees N of E at 320 km/h when it comes across a current from S of E at 115 degrees of 20 km/h. What are the airplane's new course and speed?
A plane is traveling 45 degrees N of E at 320 km/h when it comes across a current from S of E at 115 degrees of 20 km/h. What are the airplane's new course and speed?
Do you have unsolved math question and you need help? Ask a question, and we will try to solve it. We solve math question.
