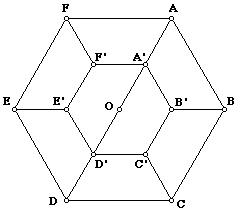
Hexagon = 8 parts
Divide the regular hexagon into eight equal parts.
Final Answer:
You need to know the following knowledge to solve this word math problem:
arithmeticbasic operations and conceptsthemes, topicsGrade of the word problem
Related math problems and questions:
- Hexagon
 Divide a regular hexagon into lines with nine completely identical parts; none of them must be in a mirror image (you can only rotate individual parts arbitrarily).
Divide a regular hexagon into lines with nine completely identical parts; none of them must be in a mirror image (you can only rotate individual parts arbitrarily). - Fractions of a Whole
 How do we call one part when we divide the whole into 5 (6,7,8,9,10) equal parts?
How do we call one part when we divide the whole into 5 (6,7,8,9,10) equal parts? - Trisection of a line segment
 Divide the line segment AB into three equal parts. Instructions: Construct an equilateral triangle ABC and find its center (e.g., the described circles).
Divide the line segment AB into three equal parts. Instructions: Construct an equilateral triangle ABC and find its center (e.g., the described circles). - Cake part remaining
 We divide the cake into 11 equal parts and eat 2 of them. Then we divide each part of the cake that is left into two more parts and eat another 2 of them. Which part of the cake did we not eat?
We divide the cake into 11 equal parts and eat 2 of them. Then we divide each part of the cake that is left into two more parts and eat another 2 of them. Which part of the cake did we not eat? - Diagonal in rectangle
 In the ABCD rectangle is the center of BC, point E, and point F is the center of the CD. Prove that the lines AE and AF divide diagonal BD into three equal parts.
In the ABCD rectangle is the center of BC, point E, and point F is the center of the CD. Prove that the lines AE and AF divide diagonal BD into three equal parts. - Dividing a Circle
 Draw a circle k, r = 4cm, and divide it into two parts in a ratio of 1:5.
Draw a circle k, r = 4cm, and divide it into two parts in a ratio of 1:5. - Strawberry portions
 Mom bought 3 kg of strawberries. He wants to divide them into eight parts and freeze them. How many kg do they have to weigh in one dose?
Mom bought 3 kg of strawberries. He wants to divide them into eight parts and freeze them. How many kg do they have to weigh in one dose?
