Thales' theorem - practice problems - last page
Instructions: Solve each problem carefully and provide a detailed solution for every item.Number of problems found: 46
- Semicircle
 The semicircle with center S and the diameter AB is constructed equilateral triangle SBC. What is the magnitude of the angle ∠SAC?
The semicircle with center S and the diameter AB is constructed equilateral triangle SBC. What is the magnitude of the angle ∠SAC? - Circumferential angle
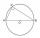
 Vertices of the triangle ΔABC lay on the circle and are divided into arcs in the ratio 10:8:7. Determine the size of the angles of the triangle ΔABC.
Vertices of the triangle ΔABC lay on the circle and are divided into arcs in the ratio 10:8:7. Determine the size of the angles of the triangle ΔABC. - Circumscribing
 Find the radius of the circumscribed circle to the right triangle with legs 6 cm and 3 cm.
Find the radius of the circumscribed circle to the right triangle with legs 6 cm and 3 cm. - OK circle
 The right triangle has hypotenuse long 33 and one cathetus long 17. Calculate the radius (circumradius) of the circle described.
The right triangle has hypotenuse long 33 and one cathetus long 17. Calculate the radius (circumradius) of the circle described. - Rectangle
 In a rectangle with sides, 8 and 9 mark the diagonal. What is the probability that a randomly selected point within the rectangle is closer to the diagonal than any side of the rectangle?
In a rectangle with sides, 8 and 9 mark the diagonal. What is the probability that a randomly selected point within the rectangle is closer to the diagonal than any side of the rectangle? - Height
 Is it true that the height is less or equal to half of the hypotenuse in any right triangle?
Is it true that the height is less or equal to half of the hypotenuse in any right triangle?
Do you have unsolved math question and you need help? Ask a question, and we will try to solve it. We solve math question.
