Infinite geometric series - practice problems
An infinite geometric series is the sum of infinitely many terms in a geometric sequence, written as a + ar + ar² + ar³ + ... where a is the first term and r is the common ratio. The series converges (has a finite sum) if and only if |r| < 1, with the sum formula S = a/(1-r). When |r| ≥ 1, the series diverges (has no finite sum). Convergent infinite geometric series appear in many applications including calculating repeating decimals (like 0.333... = 1/3), compound interest with continuous compounding, fractal geometry, and physics problems involving infinite processes. Understanding convergence and divergence is crucial for calculus, sequences and series, and mathematical analysis.Remember: Solve each problem thoughtfully and make sure to show your complete solution for every question.
Number of problems found: 32
- Flower series
 Every day, the flower develops two new flowers, and each of these new blossoms also bears two flowers each day. After eight days, how many blooms are already present in the garden?
Every day, the flower develops two new flowers, and each of these new blossoms also bears two flowers each day. After eight days, how many blooms are already present in the garden? - Geometric series
 How many terms of the geometric series 8+4+2+1+0.5+... must be taken for the sum to get within 10 to the power minus 4 of its sum to infinity?
How many terms of the geometric series 8+4+2+1+0.5+... must be taken for the sum to get within 10 to the power minus 4 of its sum to infinity? - Geometric sequence sum
 Determine s5 of the geometric sequence if: a1 + a2 = 10 and a4 - a2 = 120
Determine s5 of the geometric sequence if: a1 + a2 = 10 and a4 - a2 = 120 - Trainee triangular wedge
 Trainees stand on the marks in rows exactly 1.5 m apart. They form an expanding triangular wedge (in each subsequent row, there is one more exerciser), while the distance between the front exerciser and the back row is 30 m. Determine the number of traine
Trainees stand on the marks in rows exactly 1.5 m apart. They form an expanding triangular wedge (in each subsequent row, there is one more exerciser), while the distance between the front exerciser and the back row is 30 m. Determine the number of traine - Geometric series terms
 The sum of the first two terms of the descending geometric sequence is five quarters, and the sum of the infinite geometric series formed from it is nine quarters. Write the first three terms of the geometric sequence.
The sum of the first two terms of the descending geometric sequence is five quarters, and the sum of the infinite geometric series formed from it is nine quarters. Write the first three terms of the geometric sequence. - Horse carriage
 Hlušice and Jarošov are 10 km apart. A horse-drawn carriage leaves Hlušice for Jarošov at a speed of 5 km/h, and at the same time, a traveler leaves Jarošov for Hlušice at a speed of 3 km/h. At the moment the carriage leaves, a fly starts from the horse's
Hlušice and Jarošov are 10 km apart. A horse-drawn carriage leaves Hlušice for Jarošov at a speed of 5 km/h, and at the same time, a traveler leaves Jarošov for Hlušice at a speed of 3 km/h. At the moment the carriage leaves, a fly starts from the horse's - Geometric sequence calculation
 Determine the remaining quantities in the finite geometric sequence, given: n = 4, an = 12.5, sn = 187.5, a1 = ?, q =?
Determine the remaining quantities in the finite geometric sequence, given: n = 4, an = 12.5, sn = 187.5, a1 = ?, q =? - Annual interest
 A loan of 10 000 euros is to be repaid in annual payments over ten years. Assuming a fixed 10% annual interest rate compounded annually, calculate: (a) the amount of each annual repayment (b) the total interest paid.
A loan of 10 000 euros is to be repaid in annual payments over ten years. Assuming a fixed 10% annual interest rate compounded annually, calculate: (a) the amount of each annual repayment (b) the total interest paid. - Present value
 A bank loans a family $90,000 at a 4.5% annual interest rate to purchase a house. The family agrees to pay the loan off by making monthly payments over 15 years. How much should the monthly payment be in order to pay off the debt in 15 years?
A bank loans a family $90,000 at a 4.5% annual interest rate to purchase a house. The family agrees to pay the loan off by making monthly payments over 15 years. How much should the monthly payment be in order to pay off the debt in 15 years? - Savings
 Suppose on your 21st birthday, you begin making monthly payments of $500 into an account that pays 8% compounded monthly. If you continue the payments until your 51st birthday (30 years), How much money is in your account? How much of it is interesting? S
Suppose on your 21st birthday, you begin making monthly payments of $500 into an account that pays 8% compounded monthly. If you continue the payments until your 51st birthday (30 years), How much money is in your account? How much of it is interesting? S - Factorial division remainder
 Find the remainder after division when we divide the sum of 1! +2! +3! +. ... . +300! number 13.
Find the remainder after division when we divide the sum of 1! +2! +3! +. ... . +300! number 13. - Sum of GP members
 Determine the sum of the GP 30, 6, 1.2, to 5 terms. What is the sum of all terms (to infinity)?
Determine the sum of the GP 30, 6, 1.2, to 5 terms. What is the sum of all terms (to infinity)? - Fly and cyclist
 Two cyclists are 20 km apart on the same line. They start at the same time as each other at a speed of 10 km/hr. A fly sitting on one of the cyclist's handles starts flying toward the other cyclists at a speed of 20 km/hr. It touches the handle and moves
Two cyclists are 20 km apart on the same line. They start at the same time as each other at a speed of 10 km/hr. A fly sitting on one of the cyclist's handles starts flying toward the other cyclists at a speed of 20 km/hr. It touches the handle and moves - Exponential decay
 A tank contains 55 liters of water. Water is flowing out at the rate of 7% per minute. How long does it take to drain the tank?
A tank contains 55 liters of water. Water is flowing out at the rate of 7% per minute. How long does it take to drain the tank? - Pilsen circus
 A city citizen saw the circus's arrival in Pilsen in the morning at 08:00. He passed this information at 08:15 to three other city residents. Each of these three people then informed the other three residents at 08:30, and again at 08:45, they reported th
A city citizen saw the circus's arrival in Pilsen in the morning at 08:00. He passed this information at 08:15 to three other city residents. Each of these three people then informed the other three residents at 08:30, and again at 08:45, they reported th - Infinite sum of areas
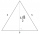 An equilateral triangle A1B1C1 is constructed above the height of the equilateral triangle ABC is constructed as. Above the height of the equilateral triangle A1B1C1 is built triangle A2B2C2, and so on. The procedure is repeated continuously. What is the
An equilateral triangle A1B1C1 is constructed above the height of the equilateral triangle ABC is constructed as. Above the height of the equilateral triangle A1B1C1 is built triangle A2B2C2, and so on. The procedure is repeated continuously. What is the - Population growth
 How many people will be on Earth from two people for 5,000 years if every couple always has four children (2 boys and two girls) at the age of 25-35, and every man will live 75 years?
How many people will be on Earth from two people for 5,000 years if every couple always has four children (2 boys and two girls) at the age of 25-35, and every man will live 75 years? - Infinite Series Equation
 Solve the given equation in the set N: 1 - x + x² - x³ + x4 - x5 +…. + = 1/3
Solve the given equation in the set N: 1 - x + x² - x³ + x4 - x5 +…. + = 1/3 - Cells - guts
 Guts (a single-celled organism) under ideal conditions divides into two littles every 27 hours on average. How many would there be in 7 days if all the childs remained alive?
Guts (a single-celled organism) under ideal conditions divides into two littles every 27 hours on average. How many would there be in 7 days if all the childs remained alive? - Infinite series
 Determine the sum of an infinite series: 1/3 + 1/9 + 1/27 + 1/81 ...
Determine the sum of an infinite series: 1/3 + 1/9 + 1/27 + 1/81 ...
Do you have unsolved math question and you need help? Ask a question, and we will try to solve it. We solve math question.
