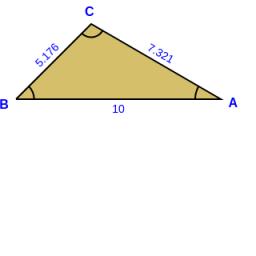
Inner angles
The inner angles of the triangle are 30°, 45°, and 105° and its longest side is 10 cm. Calculate the shortest side length, and write the result in cm up to two decimal places.
Final Answer:
Tips for related online calculators
Cosine rule uses trigonometric SAS triangle calculator.
See also our trigonometric triangle calculator.
See also our trigonometric triangle calculator.
You need to know the following knowledge to solve this word math problem:
planimetricsgoniometry and trigonometryUnits of physical quantitiesGrade of the word problem
We encourage you to watch this tutorial video on this math problem: video1
Related math problems and questions:
- In triangle 2
 In triangle XYZ, if it measures angle X=40° and measures angle Y=75°. Which is the longest side of the triangle, and why?
In triangle XYZ, if it measures angle X=40° and measures angle Y=75°. Which is the longest side of the triangle, and why? - Maturitný - RR - base
 In an isosceles triangle ABC with base AB, ∠BAC = 20°, AB = 4. The axis of the interior angle at vertex B intersects side AC at point P. Calculate the length of the segment AP. Give the result to two decimal places.
In an isosceles triangle ABC with base AB, ∠BAC = 20°, AB = 4. The axis of the interior angle at vertex B intersects side AC at point P. Calculate the length of the segment AP. Give the result to two decimal places. - Triangle's centroid
 In the triangle ABC the given lengths of its medians tc = 9, ta = 6. Let T be the intersection of the medians (triangle's centroid), and the point S is the center of the side BC. The magnitude of the CTS angle is 60°. Calculate the length of the BC side t
In the triangle ABC the given lengths of its medians tc = 9, ta = 6. Let T be the intersection of the medians (triangle's centroid), and the point S is the center of the side BC. The magnitude of the CTS angle is 60°. Calculate the length of the BC side t - Circle arc
 Calculate the circular arc area in m² where the diameter is 263 dm and the central angle is 40°. Please result round to three decimal places.
Calculate the circular arc area in m² where the diameter is 263 dm and the central angle is 40°. Please result round to three decimal places. - Interior Exterior Angles Size
 Calculate the sizes of the remaining inner and outer angles. Alpha with comma α '= 140 ° and beta with comma β' = 100 °.
Calculate the sizes of the remaining inner and outer angles. Alpha with comma α '= 140 ° and beta with comma β' = 100 °. - Area 4gon
 Calculate the area of 4-gon, two, and the two sides are equal and parallel with lengths 18, 9, 18, and 9. Inner angles are 45°, 135°,45°, 135°.
Calculate the area of 4-gon, two, and the two sides are equal and parallel with lengths 18, 9, 18, and 9. Inner angles are 45°, 135°,45°, 135°. - Tower elevation angles
 Find the height of the tower when the geodetic measured two angles of elevation α=34° 30'' and β=41°. The distance between places AB is 14 meters.
Find the height of the tower when the geodetic measured two angles of elevation α=34° 30'' and β=41°. The distance between places AB is 14 meters.
