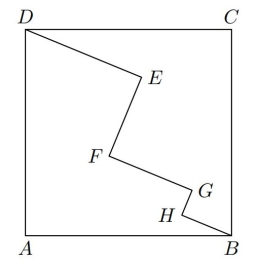
Square broken line
The vertices of the square ABCD are joined by the broken line DEFGHB. The smaller angles at the vertices E, F, G, and H are right angles, and the line segments DE, EF, FG, GH, and HB measure 6 cm, 4 cm, 4 cm, 1 cm, and 2 cm, respectively.
Determine the area of square ABCD.
Determine the area of square ABCD.
Final Answer:
Tips for related online calculators
See also our right triangle calculator.
You need to know the following knowledge to solve this word math problem:
arithmeticplanimetricsthemes, topicsGrade of the word problem
We encourage you to watch this tutorial video on this math problem: video1
Related math problems and questions:
- Circumscribed by triangle
 Inside the rectangle ABCD, the points E and F lie so that the line segments EA, ED, EF, FB, and FC are congruent. Side AB is 22 cm long, and the circle circumscribed by triangle AFD has a radius of 10 cm. Determine the length of side BC.
Inside the rectangle ABCD, the points E and F lie so that the line segments EA, ED, EF, FB, and FC are congruent. Side AB is 22 cm long, and the circle circumscribed by triangle AFD has a radius of 10 cm. Determine the length of side BC. - Square triangle area
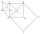 The figure shows the squares ABCD, EFCA, CHCE, and IJHE. Points S, B, F, and G are, respectively, the centers of these squares. Line segment AC is 1 cm long. Determine the area of triangle IJS. Please help...
The figure shows the squares ABCD, EFCA, CHCE, and IJHE. Points S, B, F, and G are, respectively, the centers of these squares. Line segment AC is 1 cm long. Determine the area of triangle IJS. Please help... - MO - triangles
 On the AB and AC sides of the ABC triangle lies successive points E and F, and on segment EF lie point D. The EF and BC lines are parallel. It is true this ratio FD:DE = AE:EB = 2:1. The area of the ABC triangle is 27 hectares, and line segments EF, AD, a
On the AB and AC sides of the ABC triangle lies successive points E and F, and on segment EF lie point D. The EF and BC lines are parallel. It is true this ratio FD:DE = AE:EB = 2:1. The area of the ABC triangle is 27 hectares, and line segments EF, AD, a - Segments on the hypotenuse
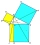 A right triangle ABC has a hypotenuse of c=26cm. How many segments does the height vc=12 cm cut out on the hypotenuse c? What are the lengths of the sides a and b? What are the angles at the vertices A and B?
A right triangle ABC has a hypotenuse of c=26cm. How many segments does the height vc=12 cm cut out on the hypotenuse c? What are the lengths of the sides a and b? What are the angles at the vertices A and B? - Quadrilateral calc
 The square ABCD is given. The midpoint of AB is E, the midpoint of BC is F, CD is G, and the midpoint of DA is H. Join AF, BG, CH, and DE. Inside the square (approximately in the middle), the intersections of these line segments form a quadrilateral. Calc
The square ABCD is given. The midpoint of AB is E, the midpoint of BC is F, CD is G, and the midpoint of DA is H. Join AF, BG, CH, and DE. Inside the square (approximately in the middle), the intersections of these line segments form a quadrilateral. Calc - Line segments
 Triangle ABC is divided by line segments. Lines DE and AB are parallel. Triangles CDH, CHI, CIE, and FIH have the same area, namely 8 dm². Find the area of quadrilateral AFHD.
Triangle ABC is divided by line segments. Lines DE and AB are parallel. Triangles CDH, CHI, CIE, and FIH have the same area, namely 8 dm². Find the area of quadrilateral AFHD. - Quadrilateral triangle segment
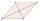 The quadrilateral ABCD is symmetrical about the diagonal AC. The length of AC is 12 cm, the length of BC is 6 cm, and the interior angle at vertex B is right. points E and F are given on the sides AB, and AD so that the triangle ECF is equilateral. Determ
The quadrilateral ABCD is symmetrical about the diagonal AC. The length of AC is 12 cm, the length of BC is 6 cm, and the interior angle at vertex B is right. points E and F are given on the sides AB, and AD so that the triangle ECF is equilateral. Determ
