Pythagorean theorem - practice problems
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This can be written as:c2 = a2 + b2
where c is the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b are the lengths of the other two sides.
Number of problems found: 1453
- Equilateral RT
 On a right triangle, side a is 12, and side b is 12. What is side c?
On a right triangle, side a is 12, and side b is 12. What is side c? - Missing side length
 Use the Pythagorean Theorem (a² + b²=c²) to find a unknown side length: a = 5; c = 13 ; b=?
Use the Pythagorean Theorem (a² + b²=c²) to find a unknown side length: a = 5; c = 13 ; b=? - Incircle to circumcircle
 Find the ratio of the areas of the incircle and the circumcircle of a square.
Find the ratio of the areas of the incircle and the circumcircle of a square. - Find area 2
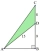 Find the area of the green region in the given picture. Dimensions are shown.
Find the area of the green region in the given picture. Dimensions are shown. - The hypotenuse
 The hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is 20 meters. If the difference between the lengths of the other sides is 4 meters, find the other sides.
The hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is 20 meters. If the difference between the lengths of the other sides is 4 meters, find the other sides. - Two circles 3
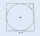 Two circles are inscribed in a square whose side is 4 cm. Find the radius of the smaller circle.
Two circles are inscribed in a square whose side is 4 cm. Find the radius of the smaller circle. - A ladder 2
 A ladder 10 m long reaches the window of a house 8 m above the ground. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the base of the wall.
A ladder 10 m long reaches the window of a house 8 m above the ground. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the base of the wall. - Isosceles right triangle
 If I have a triangle with a right angle 24 inches long on each side of the right angle what is the length of the third side?
If I have a triangle with a right angle 24 inches long on each side of the right angle what is the length of the third side? - Circle inscribed square
 What is the area of the circle that can be inscribed in a square of 10 cm?
What is the area of the circle that can be inscribed in a square of 10 cm? - Three angles
 Find all missing values of angles using the Law of Cosines if given all sides: a=12, b=13, and c=20
Find all missing values of angles using the Law of Cosines if given all sides: a=12, b=13, and c=20 - Isosceles triangle 17
 One of the equal sides of an isosceles triangle is 13 cm and its perimeter is 50 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
One of the equal sides of an isosceles triangle is 13 cm and its perimeter is 50 cm. Find the area of the triangle. - A field
 A field is in the shape of a trapezium whose parallel sides are 25 m and 10 m and the non parallel sides are 14 m and 13 m. Find the area of the field.
A field is in the shape of a trapezium whose parallel sides are 25 m and 10 m and the non parallel sides are 14 m and 13 m. Find the area of the field. - A chord 2
 A chord of length 16 cm is drawn in a circle of radius 10 cm. Calculate the distance of the chord from the center of the circle.
A chord of length 16 cm is drawn in a circle of radius 10 cm. Calculate the distance of the chord from the center of the circle. - ET inscribed circle
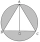 An equilateral triangle has been inscribed in a circle with a radius of 4 cm . Find the area of the shaded region.
An equilateral triangle has been inscribed in a circle with a radius of 4 cm . Find the area of the shaded region. - Cosine - legs
 Using the law of cosines, find the measurement of leg b if the givens are β=20°, a=10, and c=15.
Using the law of cosines, find the measurement of leg b if the givens are β=20°, a=10, and c=15. - Smaller square
 Let the points A, B, C and D are midpoints of the sides of the square PQRS. If the area of PQRS is 100 sq cm, what is the area of the smaller square ABCD?
Let the points A, B, C and D are midpoints of the sides of the square PQRS. If the area of PQRS is 100 sq cm, what is the area of the smaller square ABCD? - A right 3
 A right triangle has a perimeter of 300 cm . its hypotenuse is 130cm. What are the lengths of the other sides .
A right triangle has a perimeter of 300 cm . its hypotenuse is 130cm. What are the lengths of the other sides . - Rhombus 36
 Rhombus ABCD with side 8 cm long has diagonal BD 11.3 cm long. Find angle DAB.
Rhombus ABCD with side 8 cm long has diagonal BD 11.3 cm long. Find angle DAB. - General right triangle
 In a right triangle, if a =x+34 and b = x and c= 50, then solve for x. Side c is a hypotenuse. Then discuss the case when a or b is a hypotenuse.
In a right triangle, if a =x+34 and b = x and c= 50, then solve for x. Side c is a hypotenuse. Then discuss the case when a or b is a hypotenuse. - FGH right triangle
 Given a right triangle with leg lengths f and g, and hypotenuse h, if f = 7 cm and h = 11.2 cm, what is g?
Given a right triangle with leg lengths f and g, and hypotenuse h, if f = 7 cm and h = 11.2 cm, what is g?
Do you have unsolved math question and you need help? Ask a question, and we will try to solve it. We solve math question.
