Kerosene pressure difference
Kerosene (ρ1 = 830 kg . m-3) flows through the pipe. Calculate the pressure difference in the given sections when the mercury level difference (ρ2 = 13600 kg . m-3) in the mercury differential manometer is h = 2.2 dm.
Final Answer:
Tips for related online calculators
Tip: Our volume units converter will help you convert volume units.
Tip: Our Density units converter will help you convert density units.
Do you want to convert velocity (speed) units?
Tip: Our Density units converter will help you convert density units.
Do you want to convert velocity (speed) units?
You need to know the following knowledge to solve this word math problem:
Units of physical quantitiesthemes, topicsGrade of the word problem
Related math problems and questions:
- Manometer gas pressure
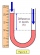 An open manometer is connected to the gas tank. The difference in water levels in both arms is 54.5 cm. The atmospheric pressure is 10 5 Pa. Calculate the gas pressure.
An open manometer is connected to the gas tank. The difference in water levels in both arms is 54.5 cm. The atmospheric pressure is 10 5 Pa. Calculate the gas pressure. - Mercury pressure
 At what depth does a hydrostatic compressive force of 3.2 MN acting on an area of 30 m² arise in mercury? (mercury density is 13,500 kg/m2)
At what depth does a hydrostatic compressive force of 3.2 MN acting on an area of 30 m² arise in mercury? (mercury density is 13,500 kg/m2) - Mercury density measurement
 10 ml of mercury has been measured to weigh 0.135 kg. Calculate the density of mercury and compare it with the density shown in the tables.
10 ml of mercury has been measured to weigh 0.135 kg. Calculate the density of mercury and compare it with the density shown in the tables. - Kerosene in the bottle
 The volume of kerosene in the bottle is 10 cm³. Find the weight of the fluid. (its density is ρ = 830 kg/m³)
The volume of kerosene in the bottle is 10 cm³. Find the weight of the fluid. (its density is ρ = 830 kg/m³) - Hydrostatic pressure
 Please calculate according to Pascal's law. Calculate the hydrostatic pressure at a depth of 300m below sea level if the density of seawater is approximately 1025kg per m³. At what depth below the surface is the hydrostatic pressure 4.5 MPa?
Please calculate according to Pascal's law. Calculate the hydrostatic pressure at a depth of 300m below sea level if the density of seawater is approximately 1025kg per m³. At what depth below the surface is the hydrostatic pressure 4.5 MPa? - Radiators
 Calculate the radiator output if it has a thermal gradient (difference between inlet water and return temperatures) a) 5°C b) 10°C c) 15°C d) 20°C A heating water volume flow is 45 kg/h. How fast the water flows from the supply pipe to the radiator e) DN1
Calculate the radiator output if it has a thermal gradient (difference between inlet water and return temperatures) a) 5°C b) 10°C c) 15°C d) 20°C A heating water volume flow is 45 kg/h. How fast the water flows from the supply pipe to the radiator e) DN1 - Melting point
 The melting point of mercury is -36°F, and its boiling point is 672°F. What is the difference between the boiling point and the melting point?
The melting point of mercury is -36°F, and its boiling point is 672°F. What is the difference between the boiling point and the melting point?
