Scalar product - practice problems
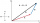
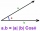
The scalar product (or dot product) of two vectors produces a scalar quantity, calculated as a·b = |a||b|cos(θ) where θ is the angle between the vectors, or as a·b = a₁b₁ + a₂b₂ + a₃b₃ in component form. The result is positive when vectors point in similar directions, zero when perpendicular (orthogonal), and negative when pointing in opposite directions. Properties include commutativity (a·b = b·a) and distributivity over addition. The scalar product is used to find vector magnitudes (a·a = |a|²), angles between vectors, projections of one vector onto another, and in testing perpendicularity. Applications span physics (work as force·displacement), computer graphics, and machine learning where it measures similarity between vectors.Direction: Solve each problem carefully and show your solution in each item.
Number of problems found: 26
- Matrices 2
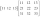 Suppose A=(1 6 3 −2) B=(4 −3 −4 3) find 2A+3B
Suppose A=(1 6 3 −2) B=(4 −3 −4 3) find 2A+3B - Calculate cuboid
 Given cuboid ABCDEFGH. We know that |AB| = 1 cm, |BC| = 2 cm, |AE| = 3 cm. Calculate in degrees the angle size formed by the lines BG and FH .
Given cuboid ABCDEFGH. We know that |AB| = 1 cm, |BC| = 2 cm, |AE| = 3 cm. Calculate in degrees the angle size formed by the lines BG and FH . - Scalar products
 The vectors a = (3, -2), b = (-1, 5) are given. Determine the vector c for which a. c = 17; b . c = 3
The vectors a = (3, -2), b = (-1, 5) are given. Determine the vector c for which a. c = 17; b . c = 3 - In plane 2
 A triangle ABC is located in the plane with a right angle at vertex C, for which the following holds: A(1, 2), B(5, 2), C(x, x+1), where x > -1. a) determine the value of x b) determine the coordinates of point M, which is the midpoint of line segment
A triangle ABC is located in the plane with a right angle at vertex C, for which the following holds: A(1, 2), B(5, 2), C(x, x+1), where x > -1. a) determine the value of x b) determine the coordinates of point M, which is the midpoint of line segment - Vectors
 Find the magnitude of the angle between two vectors u = (3; -5) and v = (10; 6)
Find the magnitude of the angle between two vectors u = (3; -5) and v = (10; 6) - Space vectors 3D
 The vectors u = (1; 3;- 4) and v = (0; 1; 1) are given. Find their sizes, calculate their angles, and determine the distances between them.
The vectors u = (1; 3;- 4) and v = (0; 1; 1) are given. Find their sizes, calculate their angles, and determine the distances between them. - Perpendicular projection
 Determine the distance of point B[1, -3] from the perpendicular projection of point A[3, -2] on a straight line 2 x + y + 1 = 0.
Determine the distance of point B[1, -3] from the perpendicular projection of point A[3, -2] on a straight line 2 x + y + 1 = 0. - Direction vector
 The line p is given by the point P [- 0,5; 1] and the direction vector s = (1,5; - 3) determines: A) value of parameter t for points X [- 1,5; 3], Y [1; - 2] lines p B) whether the points R [0,5; - 1], S [1,5; 3] lie on the line p C) parametric equations
The line p is given by the point P [- 0,5; 1] and the direction vector s = (1,5; - 3) determines: A) value of parameter t for points X [- 1,5; 3], Y [1; - 2] lines p B) whether the points R [0,5; - 1], S [1,5; 3] lie on the line p C) parametric equations - Perpendicular lines
 Points A(1,2), B(4,-2) and C(3,-2) are given. Find the parametric equations of the line that: a) It passes through point C and is parallel to the line AB, b) It passes through point C and is perpendicular to line AB.
Points A(1,2), B(4,-2) and C(3,-2) are given. Find the parametric equations of the line that: a) It passes through point C and is parallel to the line AB, b) It passes through point C and is perpendicular to line AB. - Vector v4
 Find the vector v4 perpendicular to the vectors v1 = (1, 1, 1, -1), v2 = (1, 1, -1, 1) and v3 = (0, 0, 1, 1)
Find the vector v4 perpendicular to the vectors v1 = (1, 1, 1, -1), v2 = (1, 1, -1, 1) and v3 = (0, 0, 1, 1) - Decide 2
 Decide whether points A[-2, -5], B[4, 3], and C[16, -1] lie on the same line
Decide whether points A[-2, -5], B[4, 3], and C[16, -1] lie on the same line - Vector perpendicular
 Find the vector a = (2, y, z) so that a⊥ b and a ⊥ c where b = (-1, 4, 2) and c = (3, -3, -1)
Find the vector a = (2, y, z) so that a⊥ b and a ⊥ c where b = (-1, 4, 2) and c = (3, -3, -1) - Vector equation
 Let's v = (1, 2, 1), u = (0, -1, 3) and w = (1, 0, 7). Solve the vector equation c1 v + c2 u + c3 w = 0 for variables c1, c2, c3 and decide whether v, u, and w are linear dependent or independent
Let's v = (1, 2, 1), u = (0, -1, 3) and w = (1, 0, 7). Solve the vector equation c1 v + c2 u + c3 w = 0 for variables c1, c2, c3 and decide whether v, u, and w are linear dependent or independent - Angle of the body diagonals
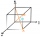 Using the vector dot product calculate the angle of the body diagonals of the cube.
Using the vector dot product calculate the angle of the body diagonals of the cube. - Parallel and orthogonal
 I need math help in this problem: a=(-5, 5 3) b=(-2,-4,-5) (they are vectors) Decompose the vector b into b=v+w where v is parallel to a and w is orthogonal to a, find v and w
I need math help in this problem: a=(-5, 5 3) b=(-2,-4,-5) (they are vectors) Decompose the vector b into b=v+w where v is parallel to a and w is orthogonal to a, find v and w - Parametric form
 Calculate the distance of point A [2,1] from the line p: X = -1 + 3 t Y = 5-4 t Line p has a parametric form of the line equation.
Calculate the distance of point A [2,1] from the line p: X = -1 + 3 t Y = 5-4 t Line p has a parametric form of the line equation. - Perpendicular and parallel
 Find the value of t if 2tx+5y-6=0 and 5x-4y+8=0 are perpendicular and parallel lines. What angle does each line make with the x-axis, and find the angle between the lines?
Find the value of t if 2tx+5y-6=0 and 5x-4y+8=0 are perpendicular and parallel lines. What angle does each line make with the x-axis, and find the angle between the lines? - Coordinates of square vertices
 The ABCD square has the center S [−3, −2] and the vertex A [1, −3]. Find the coordinates of the other vertices of the square.
The ABCD square has the center S [−3, −2] and the vertex A [1, −3]. Find the coordinates of the other vertices of the square. - Scalar product
 Calculate the scalar product of two vectors: (2.5) (-1, -4)
Calculate the scalar product of two vectors: (2.5) (-1, -4) - Equation of the circle
 Find the equation of the circle with the center at (1,20), which touches the line 8x+5y-19=0
Find the equation of the circle with the center at (1,20), which touches the line 8x+5y-19=0
Do you have unsolved math question and you need help? Ask a question, and we will try to solve it. We solve math question.
