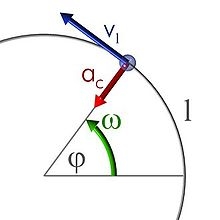
Constant Angular Acceleration
The particle began to move from rest along a circle with a constant angular acceleration. After five cycles (n = 5), its angular velocity reached the value ω = 12 rad/s.
Calculate the magnitude of the angular acceleration ε of this motion and the time interval required for the first five cycles.
Calculate the magnitude of the angular acceleration ε of this motion and the time interval required for the first five cycles.
Final Answer:
Tips for related online calculators
Do you want to convert velocity (speed) units?
Try conversion angle units angle degrees, minutes, seconds, radians, grads.
Try conversion angle units angle degrees, minutes, seconds, radians, grads.
You need to know the following knowledge to solve this word math problem:
algebraplanimetricsUnits of physical quantitiesthemes, topicsGrade of the word problem
We encourage you to watch this tutorial video on this math problem: video1
Related math problems and questions:
- Circular motion
 The mass point regularly moves in a circle with radius r = $r m angular velocity ω = 4.3 rad/s. Calculate the period, frequency, and centripetal acceleration of this movement.
The mass point regularly moves in a circle with radius r = $r m angular velocity ω = 4.3 rad/s. Calculate the period, frequency, and centripetal acceleration of this movement. - Acceleration of point
 The mass point moves evenly along a circle with a radius of 1.2 m at an angular velocity of 25 rad/s. Determine the frequency, period, and centripetal acceleration!
The mass point moves evenly along a circle with a radius of 1.2 m at an angular velocity of 25 rad/s. Determine the frequency, period, and centripetal acceleration! - Rotational motion of a cylinder
 Calculate the kinetic energy of a cylindrical body of radius r= 0.08 meter and mass m= 1.5kg at time t= 5 s, if this body rotates around an axis passing through the center of the cylinder with a constant acceleration Ԑ= 5 rad/s², if at time t=.
Calculate the kinetic energy of a cylindrical body of radius r= 0.08 meter and mass m= 1.5kg at time t= 5 s, if this body rotates around an axis passing through the center of the cylinder with a constant acceleration Ԑ= 5 rad/s², if at time t=. - Calculate
 A bicycle rotates with a frequency of f= 25 Hz. By braking, its rotation can be slowed down evenly and the bicycle stops after a time of t0= 30 s from the start of braking. Calculate the angular acceleration Ԑ and the number of revolutions the bicycle mak
A bicycle rotates with a frequency of f= 25 Hz. By braking, its rotation can be slowed down evenly and the bicycle stops after a time of t0= 30 s from the start of braking. Calculate the angular acceleration Ԑ and the number of revolutions the bicycle mak - Merry-go-round angular velocity
 Calculate the magnitude of the angular velocity of the seat of a merry-go-round moving in uniform motion in a circle with an orbital period of 0.2 minutes.
Calculate the magnitude of the angular velocity of the seat of a merry-go-round moving in uniform motion in a circle with an orbital period of 0.2 minutes. - From city 2
 A passenger train left city A for city B in the morning. At the same time, a freight train left city B for city A along the same track. Both trains traveled the entire route at constant speeds. They passed each other on the track at 9:45 a.m., the passeng
A passenger train left city A for city B in the morning. At the same time, a freight train left city B for city A along the same track. Both trains traveled the entire route at constant speeds. They passed each other on the track at 9:45 a.m., the passeng - Angular velocity
 Determine the difference in angular velocities of the clock hands. [rad/s] ω of clock hands =? ω minute hands =? ω second hands =?
Determine the difference in angular velocities of the clock hands. [rad/s] ω of clock hands =? ω minute hands =? ω second hands =?
