Physical quantity - math word problems - page 329 of 346
Number of problems found: 6913
- Unit resistance
 What is the resistance of a two-conductor line 10 m long made of 4.0 mm² aluminum wire?
What is the resistance of a two-conductor line 10 m long made of 4.0 mm² aluminum wire? - Gorilla fruit supply
 At the Prague Zoo, they need to know how long the fruit will last for the gorillas. The stock in the warehouse would last the female Kamba for 25 days, the male Richard for 20 days, and the little Nura even for 40 days. How long will the supply last if ev
At the Prague Zoo, they need to know how long the fruit will last for the gorillas. The stock in the warehouse would last the female Kamba for 25 days, the male Richard for 20 days, and the little Nura even for 40 days. How long will the supply last if ev - Triangle tangent area
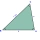 In the triangle ABC, b=5 cm, c=6 cm, /BAC/ = 80° are given. Calculate the sizes of the other sides and angles, and further determine the sizes of the tangent tc and the area of the triangle.
In the triangle ABC, b=5 cm, c=6 cm, /BAC/ = 80° are given. Calculate the sizes of the other sides and angles, and further determine the sizes of the tangent tc and the area of the triangle. - Average speed
 What is the average speed you have to move around the world in 80 days? (Path along the equator, round to km/h).
What is the average speed you have to move around the world in 80 days? (Path along the equator, round to km/h). - Cathedral roof sphere
 Cathedral height is 110 m, sphere weight 6000 kg, dome diameter 43 m, crane arm length 25 m a) what was the diameter of this sphere? b) how much mechanical work had to be done to lift it to the designated place?
Cathedral height is 110 m, sphere weight 6000 kg, dome diameter 43 m, crane arm length 25 m a) what was the diameter of this sphere? b) how much mechanical work had to be done to lift it to the designated place? - Tower distance angle
 From the smaller observation tower, we see the top of the larger tower at an elevation angle of 23°, and the difference in their heights is 12 m. How far apart are the observation towers?
From the smaller observation tower, we see the top of the larger tower at an elevation angle of 23°, and the difference in their heights is 12 m. How far apart are the observation towers? - Tree
 How tall is the tree observed at the visual angle 45°? If I stand 3 m from the tree, my eyes are two meters above the ground.
How tall is the tree observed at the visual angle 45°? If I stand 3 m from the tree, my eyes are two meters above the ground. - Subtracting complex in polar
 Given w =√2(cosine (pi/4) + i sine (pi/4) ) and z = 2 (cosine (pi/2) + i sine (pi/2) ). What is w - z expressed in polar form?
Given w =√2(cosine (pi/4) + i sine (pi/4) ) and z = 2 (cosine (pi/2) + i sine (pi/2) ). What is w - z expressed in polar form? - Parallelogram diagonal construction
 Construct a parallelogram ABCD if a=5 cm, height to side a is 5 cm, and angle ASB = 120 degrees. S is the intersection of the diagonals.
Construct a parallelogram ABCD if a=5 cm, height to side a is 5 cm, and angle ASB = 120 degrees. S is the intersection of the diagonals. - Elevation angle
 An airliner currently flying over a location 2,400 m away from the observer's location is seen at an elevation angle of 26° 20'. At what height does the plane fly?
An airliner currently flying over a location 2,400 m away from the observer's location is seen at an elevation angle of 26° 20'. At what height does the plane fly? - Performance
 Two masons with the same performance would have been made of plaster for six days. One of them, however, has increased its daily performance by 50%. How long would it take them now to make plaster together?
Two masons with the same performance would have been made of plaster for six days. One of them, however, has increased its daily performance by 50%. How long would it take them now to make plaster together? - Average speed
 The first third of the track was driven by a car at a speed of 15 km/h, the second third at a speed of 30 km/h, and the last third at a speed of 90 km/h. Find the average speed of the car.
The first third of the track was driven by a car at a speed of 15 km/h, the second third at a speed of 30 km/h, and the last third at a speed of 90 km/h. Find the average speed of the car. - A trapezoid
 A trapezoid with a base length of a = 36.6 cm, with angles α = 60°, β = 48°, and the height of the trapezoid is 20 cm. Calculate the lengths of the other sides of the trapezoid.
A trapezoid with a base length of a = 36.6 cm, with angles α = 60°, β = 48°, and the height of the trapezoid is 20 cm. Calculate the lengths of the other sides of the trapezoid. - Church tower
 Archdeacon church in Usti nad Labem has diverted the tower by 186 cm. The tower is 65 m high. Calculate the angle by which the tower is tilted. Results are written in degree minutes.
Archdeacon church in Usti nad Labem has diverted the tower by 186 cm. The tower is 65 m high. Calculate the angle by which the tower is tilted. Results are written in degree minutes. - EQL triangle
 Calculate the inradius and circumradius of an equilateral triangle with side a=67 cm.
Calculate the inradius and circumradius of an equilateral triangle with side a=67 cm. - The resistance
 What is the resistance of an aluminum wire, 0.2 km long and 10 mm in diameter?
What is the resistance of an aluminum wire, 0.2 km long and 10 mm in diameter? - Angles of elevation
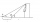 From points A and B on level ground, the angles of elevation of the top of a building are 25° and 37°, respectively. If |AB| = 57m, calculate, to the nearest meter, the distances of the top of the building from A and B if they are both on the same side of
From points A and B on level ground, the angles of elevation of the top of a building are 25° and 37°, respectively. If |AB| = 57m, calculate, to the nearest meter, the distances of the top of the building from A and B if they are both on the same side of - Water level increase
 During the experiment, water flows evenly into a cylinder-shaped container. At the end of the 5th minute of the experiment, the water level was 25% higher than at the beginning of the experiment. 0 how many percent higher will the water level be at the en
During the experiment, water flows evenly into a cylinder-shaped container. At the end of the 5th minute of the experiment, the water level was 25% higher than at the beginning of the experiment. 0 how many percent higher will the water level be at the en - Gold wire
 From one gram of gold was pulled wire 1.4 km length. What is its diameter if the density of Au is ρ=19.5 g/cm³?
From one gram of gold was pulled wire 1.4 km length. What is its diameter if the density of Au is ρ=19.5 g/cm³? - Pyramid soil
 The pit is a regular truncated 4-sided pyramid, with 14 m and 10 m base edges and a depth of 6m. Calculate how much m³ of soil was removed when we dug this pit.
The pit is a regular truncated 4-sided pyramid, with 14 m and 10 m base edges and a depth of 6m. Calculate how much m³ of soil was removed when we dug this pit.
Do you have unsolved math question and you need help? Ask a question, and we will try to solve it. We solve math question.
